里程碑:首款MASH疗法已获批,新药开发还有哪些挑战?
来源:医药观澜 | 发布时间:2025-10-31
摘要:代谢相关脂肪性肝炎(MASH)是当前最常见的慢性肝病之一,且发病率正快速上升,日益成为全球公共健康的重大威胁。近年来,MASH治疗领域迎来重要突破:首款MASH疗法已获批上市,多款基于不同作用机制的在研疗法也已进入临床后期开发阶段。为了加速MASH药物的开发,药明康德旗下生物学业务平台(WuXi Biology)已建立多款MASH疾病相关模型,并配套开发了组织学、生物标志物和临床终点的评估技术。本文将介绍WuXi Biology科学团队如何助力合作伙伴突破MASH药物早期发现和开发方面的关键挑战。
MASH药物研发的难点
2024年3月,美国FDA批准Madrigal Pharmaceuticals公司开发的Rezdiffra(resmetirom,MGL3196)上市,用于治疗成人MASH患者,标志着全球首款MASH药物的正式问世。这一里程碑激发了业界对MASH治疗领域的关注,目前已有多款基于不同作用机制的MASH在研疗法处于3期临床开发阶段。今年8月,诺和诺德(Novo Nordisk)的重磅疗法Wegovy(2.4 mg司美格鲁肽)也获得FDA的加速批准,成为首个获批用于治疗MASH的胰高血糖素样肽-1(GLP-1)疗法。
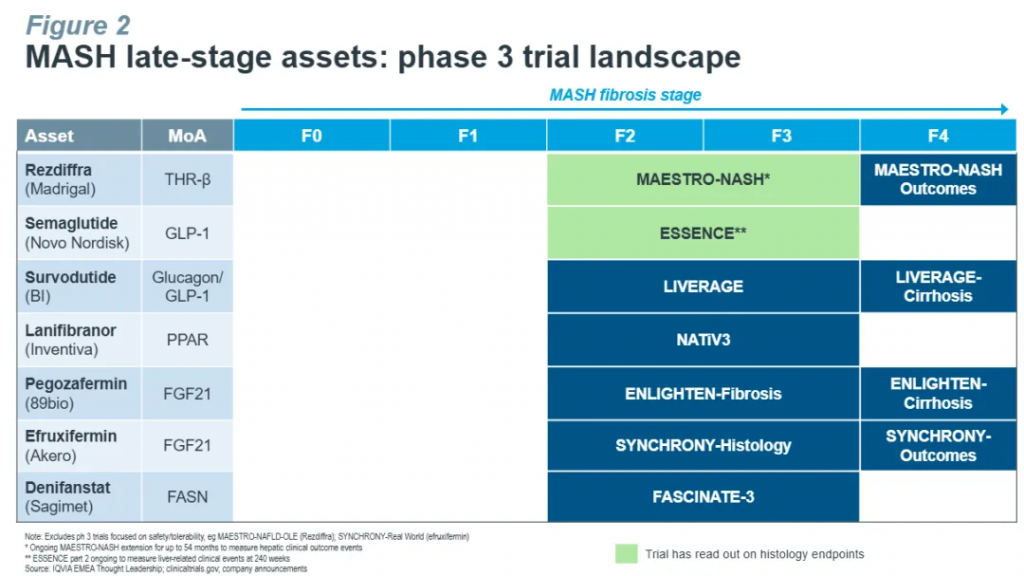
然而,MASH药物的研发之路并不平坦。在Rezdiffra获批之前,已有多家药企和生物技术公司的候选药物在临床试验中表现不佳。其核心挑战之一在于MASH的致病机制复杂,目前尚未被完全阐明。已知肝脏脂肪沉积最终可引发炎症反应与纤维化,且MASH发病机制与代谢异常密切相关,不同患者的疾病进程差异显著,受环境和遗传等多种因素的影响。这种高度复杂性和异质性也为动物模型的构建带来了巨大挑战[1]。目前虽然已经有数十种MASH小鼠模型被开发,但尚无一种模型能全面、准确地反映患者的临床表现。因此,如何选择合适的动物模型已成为MASH新药临床前研究的关键问题之一。对此,WuXi Biology的科学家针对多种MASH小鼠模型的临床相关性进行了系统评估。
如何选择合适的MASH小鼠模型评估药效
MASH患者的典型特征包括肝组织学改变和整体代谢改变两方面。其中,肝组织学改变包括脂肪变性、肝细胞气球样变、肝小叶炎症和肝纤维化。代谢改变主要包括体重上升、胰岛素抵抗和高血脂。因此,临床前动物模型能否准确预测候选药物在肝组织学和整体代谢上的改善效果,成为评价模型有效性的关键标准。
在此次研究中,WuXi Biology科学家选取了多种MASH小鼠模型,并结合多款已进入临床阶段、在公开试验中展现疗效的在研药物,系统评估各模型对候选药物临床表现的预测能力。结果显示,WuXi Biology肝病平台的多种模型能够有效重现不同候选药物在临床试验中的疗效表现。
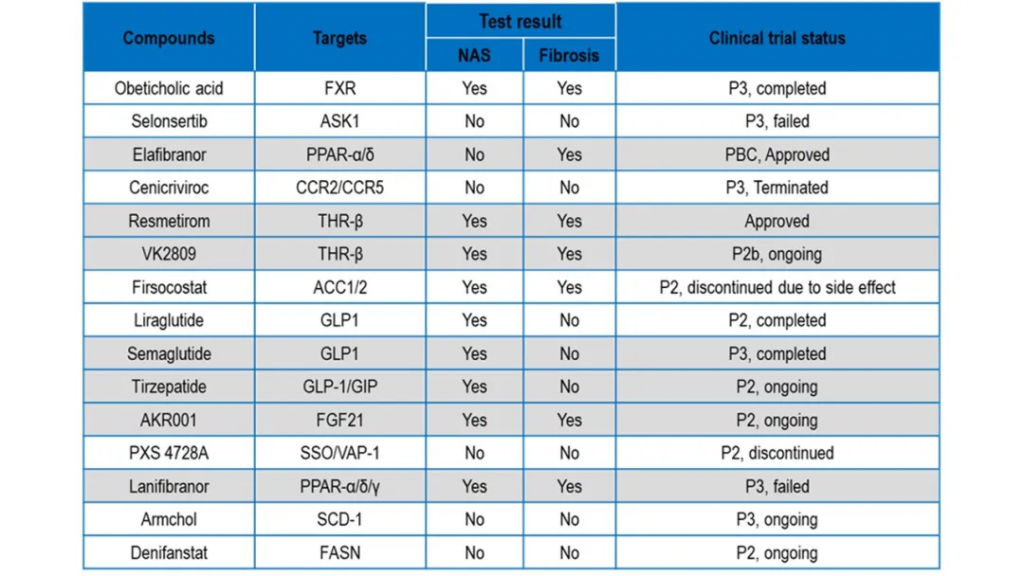
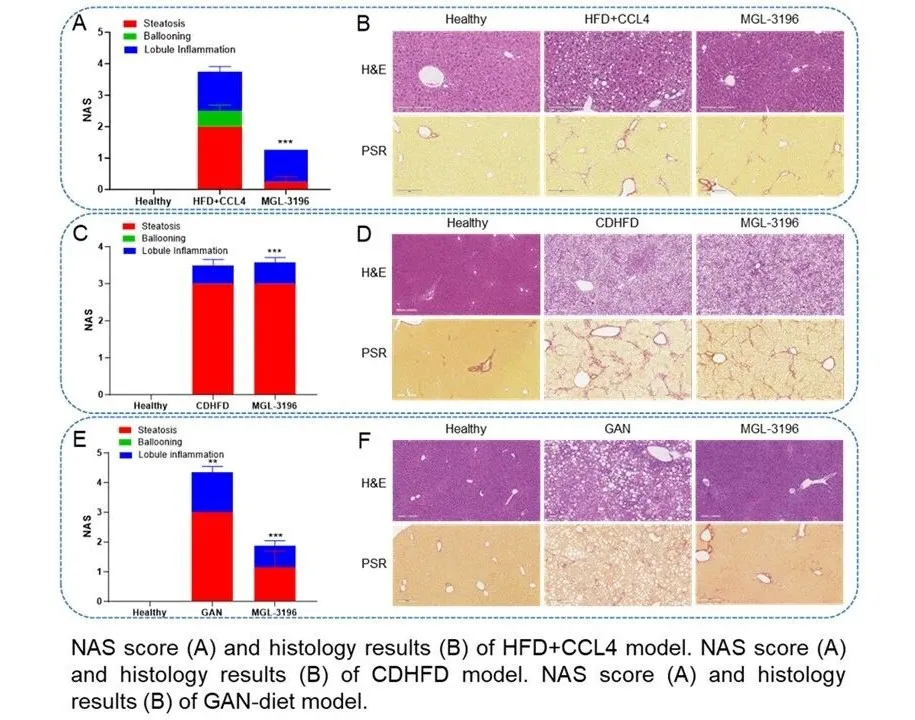
具体实验结果显示,现有的常用模型,如高脂饮食(HFD)联合四氯化碳(CCl₄)诱导的小鼠模型、胆碱缺乏饮食(CDHFD)诱导的模型以及甘氨酸-精氨酸-硝酸盐(GAN)饮食模型均可有效模拟NAS评分和纤维化评分,且resmetirom和司美格鲁肽等化合物在这些模型上均可显著改善MASH特征,这与其在临床试验中的积极结果相吻合。
然而,这些模型均存在不同的局限性,例如HFD+CCl₄模型缺乏代谢异常背景,CDHFD模型缺乏肥胖特征,而GAN饮食模型诱导周期过长。尽管有些MASH动物模型与患者的临床症状具有较高相关性,但药效评估模型的选择需要与候选药物的作用机制高度匹配。2024年发表在Nature Metabolism上的一篇文章也指出,目前还没有单一动物模型可完整模拟MASH疾病的复杂性,但通过对模型的深入表征,可以更精准地根据药物作用机制进行匹配。因此,根据不同的药物类型、作用机制及评估周期,WuXi Biology将对模型的选择提供个体化的建议,以达成最佳的药物评估效果。
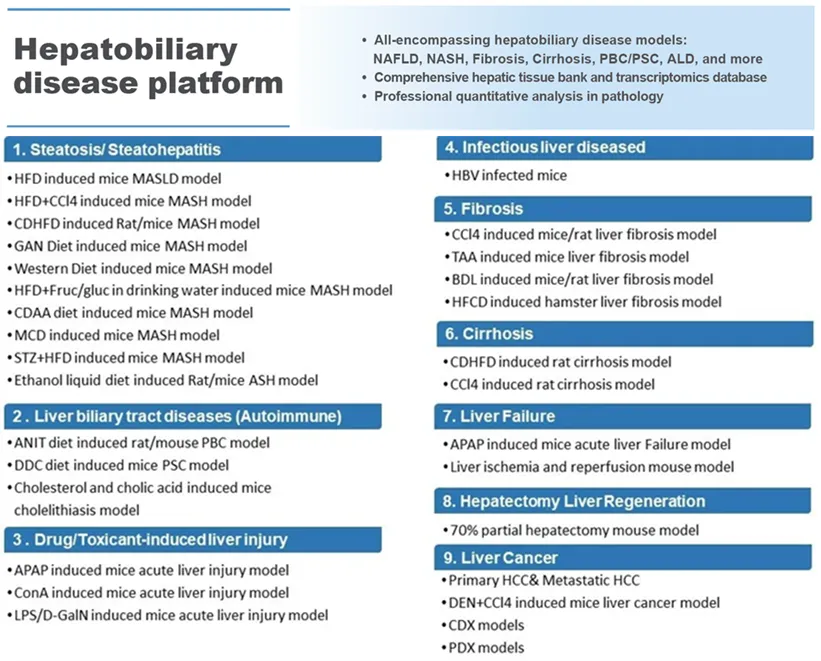
为应对MASH疾病复杂性的挑战,WuXi Biology已构建并表征多种具有不同特征的MASH动物模型,同时通过调整饲料成分和饲养环境开发新的MASH模型,支持研究人员深入理解候选药物的作用机制,并更准确评估其临床潜力。此外,平台还配备了全面的肝组织学和生物标志物检测技术,并设有通过CAP认证的病理学实验室,支持各类肝脏病理的定量分析。
除了MASH模型,WuXi Biology还建立了覆盖多种肝病类型的小鼠和大鼠疾病模型体系,包括酒精性肝炎(ASH)、代谢和酒精相关脂肪变性肝病(MetALD)、肝纤维化、肝硬化、急性/慢性肝损伤、肝功能衰竭、肝癌以及多种胆道疾病。该平台致力于提供高质量的体内药理研究服务,加速肝病新疗法的开发。目前,团队已成功为全球合作伙伴开展了涵盖不同分子类型和治疗靶点的药物测试,其中部分项目已进入临床阶段或获得FDA批准。
不仅如此,WuXi Biology还提供覆盖从靶点发现到候选分子筛选直至临床推进的全流程研究服务,可灵活支持独立或一体化项目。展望未来,药明康德将继续基于其独特的CRDMO模式,赋能合作伙伴的创新项目,致力于将更多新药、好药带给全球病患,早日实现“让天下没有难做的药,难治的病”的愿景。
CRDMO: Overcoming Early-Stage Challenges in MASH Drug Development
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) has emerged as one of the most prevalent chronic liver diseases globally, with its rising incidence posing a growing public health concern. Recent breakthroughs have renewed optimism in the field—most notably, the U.S. FDA’s March 2024 approval of Madrigal Pharmaceuticals’ Rezdiffra (resmetirom, MGL3196), the first approved therapy for MASH. This milestone has catalyzed significant momentum in drug development, with multiple candidates now in late-stage clinical trials across a variety of mechanisms.
However, the road to successful MASH therapy development remains complex and uncertain. Prior to Rezdiffra, numerous promising candidates failed clinical studies. One major obstacle is the multifactorial and poorly understood pathogenesis of MASH. Disease progression is driven by a cascade of interrelated factors—hepatic fat accumulation, inflammation, fibrosis, and systemic metabolic dysfunction—further complicated by high inter-patient heterogeneity shaped by genetics and environment. These challenges underscore the critical need for robust preclinical models to support early-stage discovery and translational success.
Enabling Predictive Preclinical Modeling at WuXi Biology
As a core capability under WuXi AppTec’s CRDMO (Contract Research, Development, and Manufacturing Organization) model, WuXi Biology has built an expansive platform of MASH-relevant in vivo models and translational tools to help partners address early-stage development challenges.
Understanding that no single model can capture the full complexity of MASH, WuXi Biology scientists have systematically evaluated a range of mouse models for their predictive performance using drug candidates already in clinical development. These models were assessed for their ability to replicate key human disease features, including:
- Liver histological changes: steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning, lobular inflammation, and fibrosis
- Metabolic disturbances: insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and weight gain
In comparative studies, several models—such as the high-fat diet (HFD) plus carbon tetrachloride (CCl₄), choline-deficient high-fat diet (CDHFD), and glycine-arginine-nitrate (GAN) diet models—effectively reproduced key clinical endpoints, including NAFLD activity scores (NAS) and fibrosis stages. Investigational compounds such as resmetirom and semaglutide showed concordant efficacy in these models, mirroring their clinical trial performance.
Precision Model Selection Tailored to Drug Mechanism
Despite their utility, each model has limitations. For instance:
- HFD+CCl₄: lacks a background of metabolic abnormalities
- CDHFD: fails to induce obesity
- GAN: requires an extended induction period
As no single model can fully recapitulate the MASH disease landscape, WuXi Biology emphasizes mechanism-matched model selection. This strategy aligns animal model characteristics with the candidate drug’s mode of action, improving translational fidelity. A recent Nature Metabolism article (2024) reinforces this approach, advocating for in-depth model characterization to maximize predictive relevance.
To this end, WuXi Biology has developed customizable MASH models by fine-tuning dietary compositions and housing conditions. These tools are supported by robust histological, biomarker, and endpoint assessment capabilities, including a CAP-certified pathology lab for quantitative liver pathology analysis.
A Comprehensive Liver Disease Modeling Ecosystem
Beyond MASH, WuXi Biology’s platform spans a broad range of liver diseases in both mice and rats, including:
- Alcohol-associated steatohepatitis (ASH)
- Metabolic and alcohol-associated liver disease (MetALD)
- Liver fibrosis and cirrhosis
- Acute and chronic liver injury
- Liver failure and hepatocellular carcinoma
- Biliary tract diseases
This full-spectrum capability enables partners to explore diverse therapeutic mechanisms and molecular modalities. To date, the platform has supported numerous global drug discovery programs, some of which have advanced into clinical development or achieved regulatory milestones.
Empowering Innovation Through Integrated CRDMO Solutions
WuXi Biology also offers end-to-end research services, encompassing target validation, hit discovery, lead optimization, and preclinical evaluation—flexibly supporting both standalone studies and integrated CRDMO programs. This seamless infrastructure accelerates candidate progression from discovery to IND-enabling studies.
Looking ahead, WuXi AppTec remains committed to driving innovation in liver disease research through its integrated CRDMO model. By providing scientific insight, advanced technologies, and tailored model systems, WuXi Biology helps global partners de-risk early-stage development and bring transformative therapies to patients worldwide, realizing the mission of making drug development easier and diseases easier to treat.