What to expect from medtech in 2024
来源:麦肯锡 | 发布时间:2024-03-12
The medtech industry posted an uneven year in 2023. Among the reasons for celebration were expectation-beating revenue growth, a record number of novel-product approvals, and a spate of divestitures that helped companies refocus on their core capabilities.
On the flip side, the growing popularity of glucagon- like peptide-1 (GLP-1) drugs for weight loss led investors to move away from many obesity-related- device stocks. Profitability did not meet investor expectations in an environment where margins increasingly became a key point of focus for valua- tions. And companies continued to struggle to perform consistently across geographies, especially outside the United States.
Indeed, 2023 marked the fourth consecutive challenging year for medtech, following a boom from 2012 to 2019 1 Despite many advances, a value creation slowdown may force companies to make bold moves to reset their trajectories in response to investor skepticism and other macroeconomic headwinds.
Since the September 2023 publication of our com- prehensive report Medtech Pulse: Thriving in the next decade, we have spoken to more than 200 medtech executives. In this article, we draw from the insights and questions that emerged from those conversations and offer seven predictions about the evolving industry landscape in the coming year.
1. Industry growth will likely stabilize at a higher level than the prepandemic average
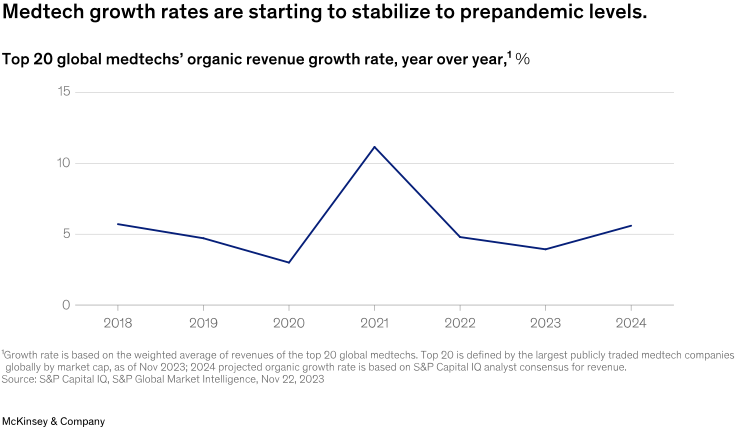
Growth in medtech has accelerated since the COVID-19 pandemic, bringing with it higher expec- tations for medtech companies. The uptick in patient volumes due to the pandemic dampened in 2023. Other underlying growth factors driving patient volumes continue to persist, though, including demographic shifts because of aging populations and the availability of innovative technologies that address high unmet needs across such disease areas as diabetes, heart failure, and stroke. Growth is also being fueled by patients accessing new and nontraditional sites of care, including alternative surgery centers (ASCs), medical offices, and outpatient settings.
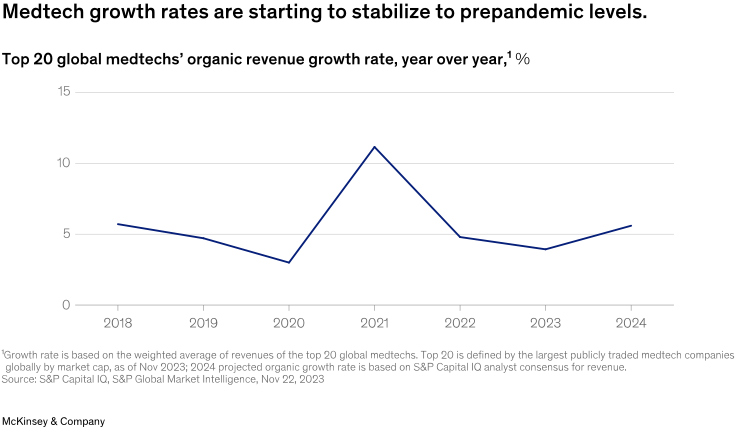
Going into 2024, we expect overall medtech revenue growth to stabilize at 100 to 150 basis points above prepandemic rates (Exhibit 1).
And as industry leaders look forward to the next five years, cardiovascular health, digital healthcare, and robotics are expected to be among the fastest-growing segments.
These trends present several hurdles for medtech companies. First, as market growth rises, companies will find it more challenging to outperform expec-tations. Second, the widening growth rates between segments will require conglomerates to reallocate resources more thoughtfully. And third, the race to serve ASCs, medical offices, and outpatient settings will continue to intensify.
2. Investors will continue to seek profitable growth
While sales growth remains chief in value creation, profitability and cash flow are increasingly coming into focus. The correlation between profit margin improvement and valuation has almost tripled since 2019 3 The top-quartile value creators in medtech improved their profitability in the past two years and are expected to continue expanding EBITA margins by at least 200 basis points over the next two years.
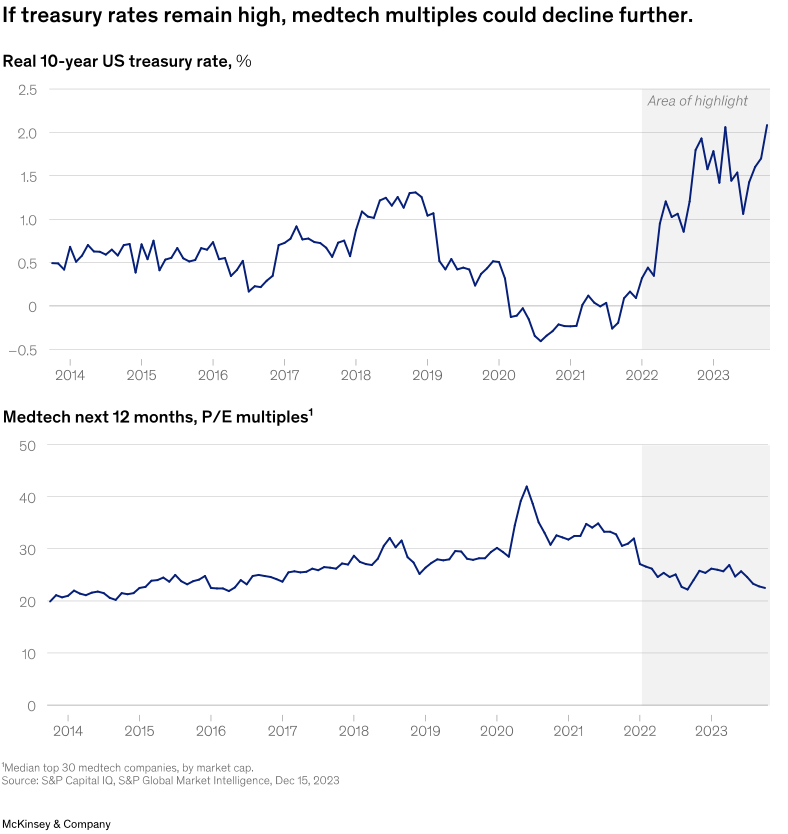
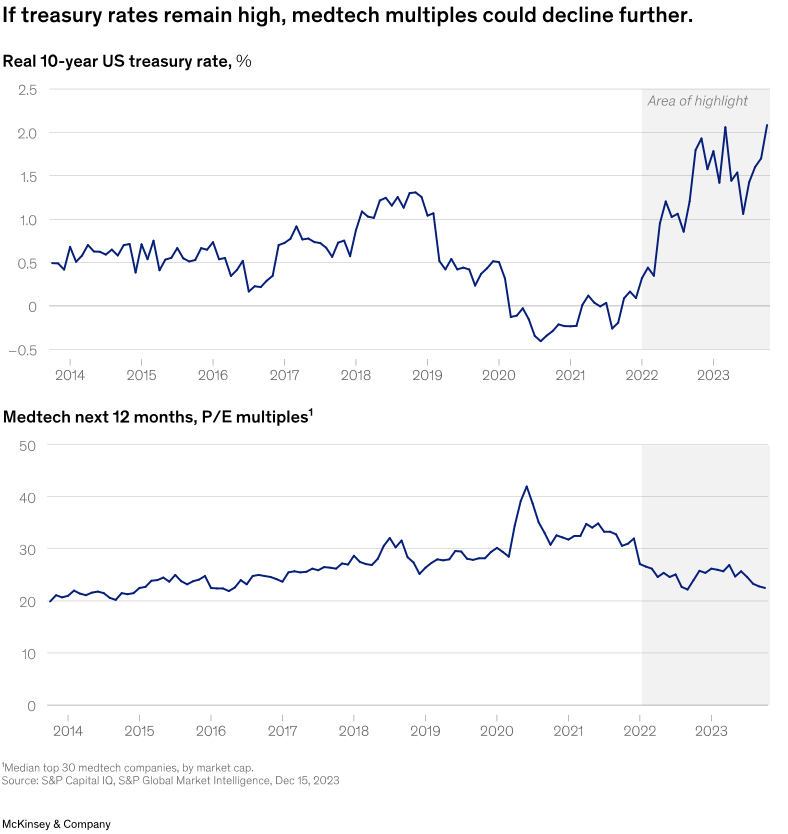
In conversations with medtech executives on profitability, we heard a common refrain: margin expansion will decrease in importance when interest rates decline. Historically, this line of thinking has been true. From 2014 to 2022, medtech valuations were inversely correlated with real treasury rates (Exhibit 2); as interest rates declined, investors focused more on revenue growth than on earnings growth, and valuations rose.
However, valuations have never been as disconnected from real rates as they have been in the past 18 months: even as interest rates rose dramatically, medtech valuations declined only modestly. As such, the expected decline in interest rates in 2024 may not necessarily boost medtech valuations. Against this macrodynamic,investors will remain keenly focused on companies’ ability to expand margins.
3. The industry will deliver another banner year for innovation
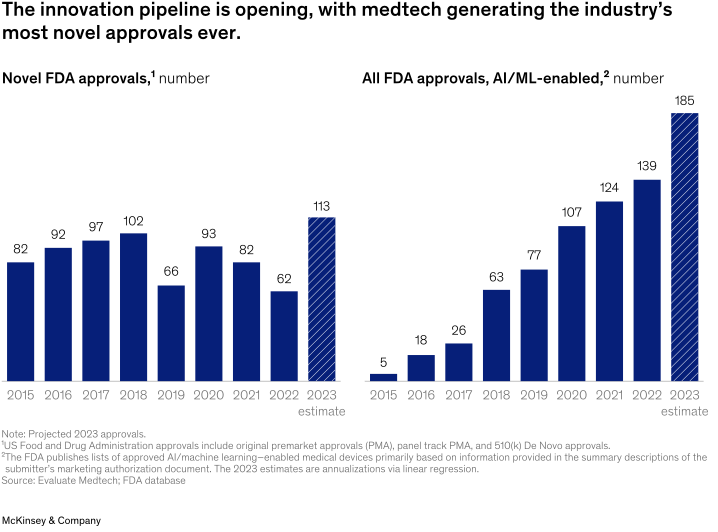
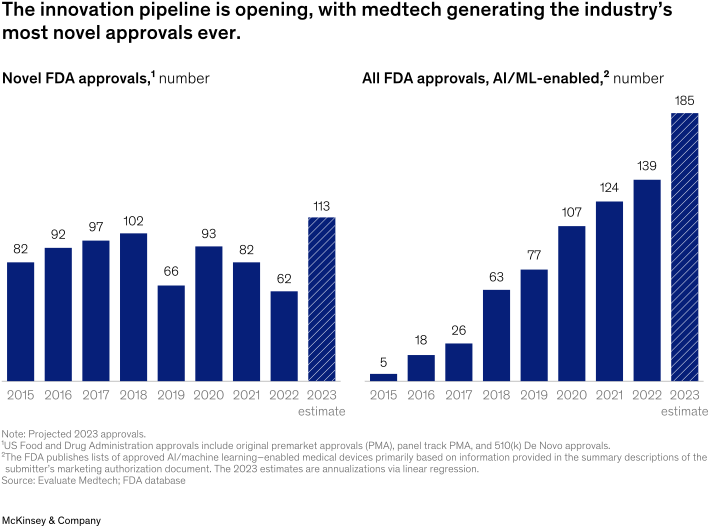
In 2023, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved more novel medical technologies than it has in any single year ever before (Exhibit 3). Several factors contributed: approvals of AI and machine-learning-enabled medtech products reached an all-time high; miniaturization and improved visualization continued to drive approvals in cardiovascular and urology segments, among others; and digitally enabled categories, such as neuromodulation and robotics, continued to grow steadily. Also, waiting times for FDA reviews receded by almost 15 percent from 2020 to 2022
Based on our conversations with medtech execu-tives, we expect the pace of innovation in 2024 to exceed 2020 to 2022 levels, with cardiovascular,digital-health-device, and neuromodulation segments gaining momentum. Advanced imaging,microelectronics, miniaturization, and new treatment modalities, such as renal denervation, are spurring innovation in underserved disease areas. These exciting advances can fuel the next wave of growth and improvements in patients’ quality of life. The pace of innovation also means more competition for medtech companies. Increasingly, it’s the big, novel innovations that will drive commercial relevance and growth—incrementalism won’t be enough.
4. Performance across geographies will continue to be lumpy
In 2024, we project that China, Japan, and the United States will contribute two-thirds of near-
term industry growth in medtech. Across more established markets, such as Japan and the United States, growth continues to be driven by innovation and the adoption of innovative technologies. In the United States, commercial execution and innovation will be the hallmarks of growth.
The market in Japan will likely behave similarly,though CFOs and finance leaders there will need to be thoughtful about managing currency risk (for example, through hedging strategies). Domestic and international companies are facing foreign-exchange challenges in Japan, making the US market even more critical to overall industry growth.
Growth in Europe will likely slow after a year in which price increases saw a step-up in the underlying growth rate. Medtech companies that thrive in the European market will tap fresh solutions to help providers manage workforce shortages and improve health economics through reduced readmissions and shorter hospital stays.
Elsewhere, medtech leaders are tackling difficult strategic choices. China has delivered tremendous growth over the past decade. However, increasing complexity, local competition, and volume-based procurement have posed challenges for multinational corporations. India will begin to make a bigger splash, thanks to favorable governmental-policy changes, increased investment flow, a maturing tech ecosystem, and the emergence of growing local businesses that are increasing provider access to technology and training.
5. Leaders in AI adoption will start to see benefits of scale
The underlying technologies of generative AI (gen AI)—namely, foundational models—have a long history in life sciences and medtech. Foundational models representing complex structures have already been used in many insight-generating tasks, particularly in product development. For example,digital-twin technologies (virtual representations of physical medtech devices paired with deep-learning models) have been used to validate alternative, and more effective, device designs. Most of the gen-AI- related activity in medtech to date has focused on device enablement, functionality, and R&D, with untapped opportunities in commercial, supply chain, and other business functions.
Medtech companies that adopt gen AI are starting to gain productivity benefits, starting with low-hanging fruit such as “copilots” for workers in HR, IT, finance, and legal roles. Companies are beginning to explore the impact of gen AI on commercial and operational roles. Because of regulatory require-ments, the deep integration of AI in medical products and services remains years away. However, some companies will start integrating gen AI into their products and software, such as by leveraging voice prompts. New capabilities and talent will be needed to capture the business value fully. Given the rapid pace of innovation, early adopters are likely to have an advantage over the competition.
6. M&A deal volumes will likely remain stable, with a continued balance of growth and at-scale transactions
Medtech M&A slowed in 2023 amid earnings challenges, macroeconomic uncertainty, and rising interest rates. Meanwhile, large buyers set a precedent of paying premiums at or above 52-week highs 5 Many of these buyers were in pursuit of meeting rising growth expectations and unlocking margin expansion.
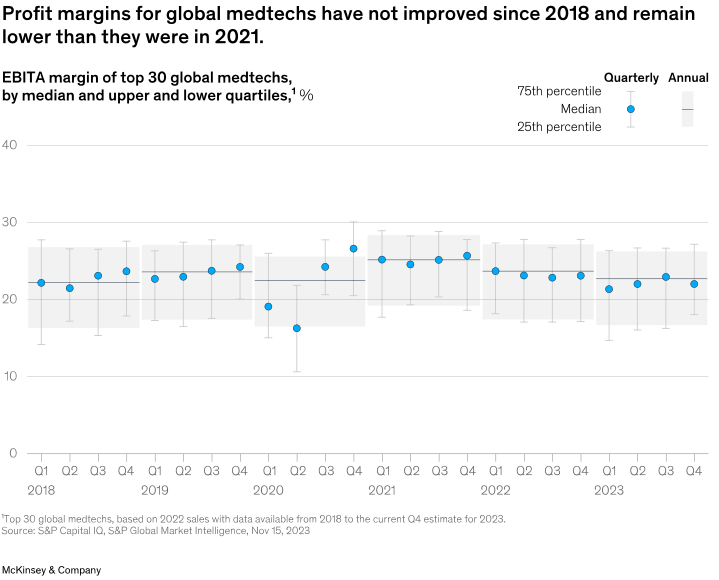
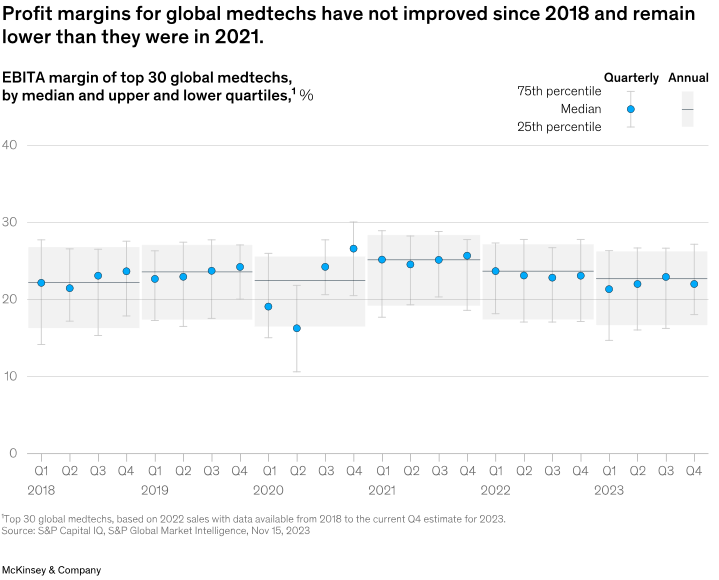
While growth-focused tuck-in deals will remain critical to value creation, they are not always available to companies at attractive valuations. Another tool that companies are increasingly exploring is at-scale transactions. Larger acquisitions can offer operating leverage, which can help medtech companies improve margins that currently sit near 2018 levels (Exhibit 4); they can also help companies in lower-growth markets improve their commercial presence with more end-to-end solutions that help care teams streamline operations and focus on patient care.
We anticipate that the volume of M&A activity will remain low but that the deals that are executed will show more balance across deal sizes. Medtech companies continue to have “dry powder” that accumulated during the COVID-19 pandemic, with approximately $55 billion of cash and cash equivalents 6 However, high-growth, at-scale, and profitable targets remain scarce. Interested acquirers will need to act quickly, given the scarcity of options.
7. Penetration of GLP-1 drugs will continue but is unlikely to have meaningful impact on medtech growth
GLP-1 therapies have been deployed to treat type 2 diabetes since 2005. Recently, their indications have expanded to obesity, and emerging data suggest that these drugs could help even more patients, including those with cardiovascular or chronic kidney disease. The market has responded, with shares of GLP-1 drug manufacturers rising 26 percent in two months after trial readouts 7 At the same time, medtech stocks, particularly those that are obesity related and in adjacent categories (such as cardio- vascular health, diabetes, orthopedics, sleep apnea, and surgery), dipped 17 percent amid concerns that GLP-1 therapy adoption will dramatically reduce the need for device-enabled diagnostics and interventions Indeed, GLP-1 drugs may meaningfully aid many patients, but they will likely have minimal effect on most medtech markets. Long-term use of GLP-1 therapy will depend on patient adherence to the prescription, payer coverage, and prescription rates. Our analysis across scenarios suggests that, for most indications across medtech sectors, low-single- digit percentages of patient populations will become long-term users of the therapy. In the meantime, GLP-1 drugs are much on the mind of analysts, executives, investors, and patients, so medtech companies will need proactive, fact-based narratives to describe the potential business impacts.
While reflecting on the past year’s growth and challenges, industry leaders have reason to be energized by the promise of 2024. The new year will bring innovations that improve more lives,opportunities to create value, and fresh approaches that adapt to market-shaping trends. Althoughobstacles remain, the medtech industry is poised to continue to deliver benefits to all its stakeholders.
这样看2024年的全球医疗器械行业
2023年,医疗科技产业经历了动荡的一年。
一方面,超出预期的收入成长、创纪录的新产品批准数量,以及企业重新专注于核心能力,开启大量资产剥离等方面值得欣喜;
另一方面,由于减肥药GLP-1药物的日益普及,导致一些投资者放弃了许多与肥胖相关的医疗器械股票。再者,在利润率日益成为估值关键点的当下,医疗科技公司的获利能力并未达到投资者的预期。它们仍然难以在各个地区保持一致的业绩增长,尤其是在美国以外的地区。
事实上,继2012年至2019年的产业繁荣之后,对于医疗科技而言,2023年是继续充满挑战的一年。尽管产业取得了许多进展,但价值创造放缓可能迫使企业采取大胆行动,重新调整发展轨迹,以应对投资者的怀疑和其他不利的宏观经济因素。
值此契机,麦肯锡于去年9月份发布《把握医疗科技脉搏:未来十年蓬勃发展》报告后,又与200多名医疗科技高管进行了交谈。通过这些对话,麦肯德得出了关于产业的见解,并从中汲取灵感,对来年不断变化的产业格局提出了7项预测,写就此文。
医药魔方Invest也对该文章进行了编译,以期给中国医疗科技产业带来启示。
产业增长可能稳定高于疫情前的平均水平
自新冠大流行以来,医疗技术的加速成长给医疗科技公司带来了更高的期望。
2023年,新冠患者数量增长受到抑制。但推动患者数量增长的其他潜在因素仍继续存在,包括人口老龄化、以及在糖尿病、心衰和中风等需求未被满足的领域出现了创新技术所导致的人口结构变化;另外,随着新的非传统护理场所,包括流动的门诊手术中心(ASC)、医疗办公室和门诊设施出现,也推动了患者数量增长。
进入2024年,我们预计医疗科技产业整体收入将稳定在比疫情前高出100至150个基点的水平(图表1)。展望未来五年,心血管健康、数位医疗和机器人技术预计将成为成长最快的领域。
图表1
不过,这些趋势也会医疗科技公司带来了一些挑战。首先,随着市场成长,公司将会发现超越预期更具挑战性。其次,各细分市场之间不断扩大的增长率将要求企业集团能更深思熟虑地重新分配资源。再者,为ASC、医疗办公室和门诊机构提供服务的竞争也将持续激烈。
投资者将继续寻求获利
虽然销售业绩增长仍是价值创造的主要因素,但获利能力和现金流也日益成为投资者关注的焦点。
自2019年以来,利润率改善与估值之间的相关性几乎增加了两倍。医疗科技领域排名前四分之一的价值创造者在过去两年中提高了获利能力,预计未来两年EBITA利润率将继续扩大至少200个基点。
在与医疗科技公司高管讨论获利能力时,我们听到了一个说法:当利率下降时,利润扩张的重要性就会降低。从历史上看,这种思路是正确的。从2014年到2022年,医疗科技的估值与实际国债利率呈负相关(图表2);随着利率下降,投资者更专注于收入增长而非获利,估值上升。
图表2
然而,在过去18个月里,估值却与实际利率脱节:即使利率大幅上升,医疗科技估值也仅小幅下降。因此,我们预计2024年利率下降不一定会提振医疗科技估值。在这种宏观形势下,投资者将继续密切关注公司扩大利润率的能力。
产业将迎来创新辉煌的一年
2023年,美国FDA批准的新型医疗技术比以往任何一年都多(图表 3)。我们认为有几个因素促成了这一点:运用人工智能和机器学习的医疗器械产品批准量达到历史最高水平;继续推动心血管和泌尿科等领域的小型化产品和迭代创新的可视化产品的批准;神经调节和机器人等数字化产品持续稳定成长。此外,从2020年到2022年,FDA审查的等待时间减少了近15%。
图表3
根据我们与医疗科技公司高管的对话,我们预计2024年的创新水平将超过2020年至2022年,心血管、数位健康设备和神经调节领域将获得发展势头。先进的影像、微电子、小型化和新的治疗方式(例如肾交感神经消融术)正在刺激相关领域的创新。
这些令人兴奋的进步可以推动下一波创新成长和患者生活质量的改善。只是,创新的步伐也意味着医疗科技公司面临更多竞争。越来越多的大型创新将推动产品商业化和市场成长——遵循渐进主义是不够的。
各地区业绩增长表现不一
到2024年,我们预计中国、日本和美国将贡献医疗技术近期产业增长的三分之二。在日本和美国等更成熟的市场,技术的创新和不断被采用将继续推动市场增长。
细分来看,在美国,商业落地和创新将成为成长的象征。日本市场也可能表现类似,尽管日本公司的CFO和财务高管需要深思熟虑地管理货币风险(例如,采用对冲策略)。
事实上,无论是日本国内的公司还是国际公司,都在面临着外汇挑战,这使得美国市场对整个产业的成长变得更加重要。
而过去一年的通胀、价格上涨等经济表现,包括欧洲医院级的招标和合同政策规定,医疗科技公司不得不增加商业投资,才可为欧洲医疗机构提供产品和服务等因素,则可能使欧洲的成长放缓。
欧洲市场那些蓬勃发展的医疗科技公司将利用新的解决方案来帮助解决劳动力短缺问题,并通过减少再入院和缩短住院时间来改善卫生经济。
于其他地方而言,领头的医疗科技企业则正在应对艰难的策略选择。过去十年,中国取得了巨大成长。然而,市场日益增加的复杂性、本土竞争和带量采购都给跨国公司带来了挑战。
印度市场将开始掀起更大的波澜,这归功于有利的政策变化、投资资金的涌入、成熟的技术生态系统以及更多本土企业的出现。
AI领域的领导者将看到规模化带来的好处
生成式人工智能 (gen AI) 的底层技术(即基础模型)在生命科学和医疗技术领域有着悠久的历史。目前,一些基础模型已被用于许多产出洞察的任务,特别是在产品开发中。例如,数位孪生技术(实体医疗科技设备与深度学习模型相结合)已被用于验证可替代且更有效的器械设计。
迄今为止,医疗技术领域大多数与人工智能相关的活动都集中在设备赋能、功能和研发上,在商业、供应链和其他业务功能方面还有尚未开发的机会。
采用新一代人工智能的医疗科技公司正在获得生产力优势,例如为人力资源、IT、财务和法律职位的员工提高效率。很多公司也开始探索新一代人工智能对商业和运营角色的影响。
由于监管要求,人工智能在医疗产品和服务中的深度整合还需要数年时间。不过,一些公司正把人工智能整合到他们的产品和软件中,例如使用语音提示。对于该行业而言,新的能力和人才是亟需的,它们可以充分捕捉业务价值。眼下,考虑到创新发展的速度,率先入局者可能在竞争中会更有优势。
并购交易量可能保持稳定
由于盈利挑战、宏观经济不确定性和利率上升,2023年医疗科技并购放缓。同时,大买家开创了在52周高点或以上溢价支付的先例。其中有许多买家是在追求满足不断增长的成长预期并释放利润扩张。
虽然以增长为重点的嵌入式收购对于价值创造仍然至关重要,但它们并不总是适用于估值具有吸引力的公司。
现在,该领域的公司正在更多地探索另一个方式,即规模交易。因为更大规模的收购不仅可以提供运营杠杆,这能够帮助医疗科技公司提高目前的利润率——眼下,这一数字仅接近2018年的水平。(图表4);还可以通过更多端到端的解决方案帮助低增长的公司改善其商业形象,帮助简化运营其医疗团队并专注于患者管理。
图表4
我们预计并购交易量将保持在较低水平,但这些执行的交易将在不同交易规模之间表现出更多的平衡。疫情期间,医疗科技公司都积攒下了一定的资金,约有550亿美元的现金和现金等价物。然而,高增长、规模大和已经盈利的目标仍然稀缺。因此,有兴趣的收购者需要抢先采取行动。
GLP-1药物对医疗技术发展影响可能有限
自2005年以来,GLP-1疗法已被用于治疗2型糖尿病。最近,它们的适应症已扩展到肥胖,并且新出现的数据表明这些药物可以帮助更多患者,包括患有心血管或慢性肾脏疾病的患者。
市场也做出了回应:试验结果公布后两个月内,GLP-1药厂的股价上涨了26%。同时,医疗科技股,尤其是那些与肥胖相关和相邻类别(如心血管健康、糖尿病、骨科、睡眠呼吸中止症和手术)的股票下跌了17%,因为人们担心GLP-1疗法的采用将大大减少需要器械的诊断和介入。
事实上,GLP-1药物给许多患者带来了有意义的帮助,但它们对大多数医疗技术市场的影响可能有限。
GLP-1疗法的长期使用将取决于患者对处方的依从性、医保和处方率。我们对各种情况的分析表明,对于医疗技术领域的大多数适应症,低个位数百分比的患者群体将成为GLP-1疗法的长期使用者。同时,分析师、高级主管、投资者和患者都非常关注GLP-1 药物,因此医疗科技公司需要积极主动、基于事实来描述对潜在业务的影响。
在反思过去一年成长和挑战的同时,产业领导者有理由对2024年的承诺感到振奋。新的一年将带来更多改善生活的创新、创造价值的机会以及适应市场趋势的新方法。尽管挑战仍然存在,但医疗技术行业已准备好继续为其所有利益相关者带来价值。